LightSpeed Fastq to Germline Variants
The LightSpeed Fastq to Germline Variants tool is designed to provide variant calls from raw sequencing data within a very short timeframe.
The tool can perform read trimming, mapping, deduplication, local realignment and germline variant calling. For a description of each step, see LightSpeed Methods.
LightSpeed Fastq to Germline Variants can only analyze one sample per analysis start. To analyze samples in batch, LightSpeed Fastq to Germline Variants must be included in a workflow. Template workflows for LigthSpeed analysis are available (see Template Workflows), but it is also possible to create custom workflows. Read about workflows here http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Workflows.html.
To run the LightSpeed tool go to:
Tools | LightSpeed (![]() ) | LightSpeed Fastq to Germline Variants (
) | LightSpeed Fastq to Germline Variants (![]() )
)
If you are connected to a CLC Server via your Workbench, you will be asked where you would like to run the analysis. We recommend that you run the analysis on a CLC Server when possible.
In the first wizard step, specify fastq files and a reference sequence (figure 3.1):
- Input data
- Reads (fastq) Fastq files for analysis. At least two fastq files representing R1 and R2 reads must be provided.
- References
- References The reference sequence that reads will be mapped to.
- Reference masking
- No masking Reads are mapped to the full reference sequence.
- Exclude annotated Reads are mapped to the full reference sequence except regions specified in the masking track.
- Include annotated only Reads are only mapped to the regions specified in the masking track.
- Masking track The track specifying the masking regions.
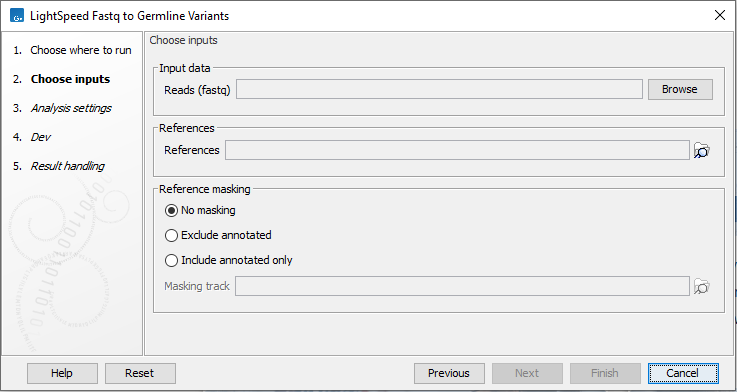
Figure 3.1: Input fastq files and references, and, optionally, a track for reference masking.
Next, options are available for trimming, read mapping and variant calling (figure 3.2):
- Trimming
- Quality trim Reads are trimmed for low quality nucleotides.
- Minimum read length after quality trim Trimmed reads shorter than this length are removed.
- Adapter trim Reads are trimmed for read-through adapter sequence.
- Minimum read length after adapter trim Trimmed reads shorter than this length are removed.
- Mapped read handling
- Remove duplicate mapped reads Reads likely representing PCR duplicates are collapsed.
- Realign mapped reads Regions of the read mapping that may be improved through local realignment are realigned.
- Variant detection
- Restrict calling to target regions Optional. A track defining where variants are called.
- Ignore non-specific matches Reads that map equally well to more than one genomic position, are not used for variant calling.
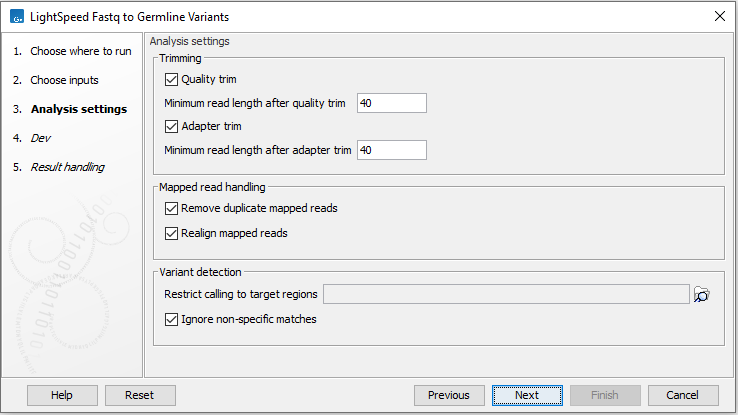
Figure 3.2: Options for trimming, deduplication and local realignment.
In the final wizard step, choose which outputs should be generated and whether results should be saved or opened. If a reads track is selected as output, runtime will be significantly increased.
Subsections
