Signal Peptide Prediction (SignalP 6.0)
The Signal Peptide Prediction (SignalP 6.0) tool uses the SignalP 6.0 service at https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/SignalP-6.0 [Teufel et al., 2022].
The SignalP 6.0 [Teufel et al., 2022] service uses a machine learning model to detect all five signal peptide types. It is also applicable to metagenomic data. Read about the SignalP history and updates at https://communities.springernature.com/posts/signalp-6-0-predicts-all-five-types-of-signal-peptides-using-protein-language-models.
To run a Signal Peptide Prediction (SignalP 6.0) analysis from the Workbench, go to:
Tools | Classical Sequence Analysis (![]() ) | Protein Analysis (
) | Protein Analysis (![]() ) | Signal Peptide Prediction (SignalP 6.0) (
) | Signal Peptide Prediction (SignalP 6.0) (![]() )
)
In the first wizard step, you select the peptide sequences to be analyzed (figure 2.1). Note: To successfully use the Signal Peptide Prediction (SignalP 6.0) service, protein sequences should not be shorter than 10 amino acids. The system may time out when more than 100 entries are provided, although the maximum allowed is 1000 sequences.
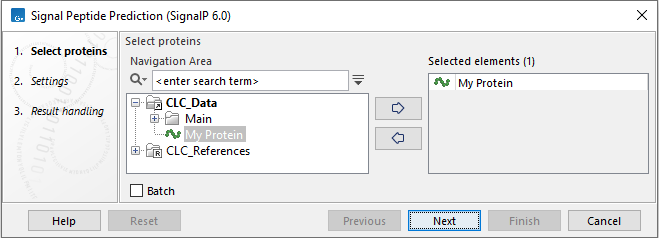
Figure 2.1: Select input protein sequences.
In the Settings wizard step, the options for SignalP 6.0 can be specified (figure 2.2). These are:
- Organism
- Eukarya Use for analyzing Eukarya. When analyzing Eukarya, only "standard" secretory signal peptides transported by the Sec translocon and cleaved by Signal Peptidase I (Lep) are predicted.
- Other Use for analyzing Archaea, Gram-positive Bacteria and Gram-negative Bacteria.
- Model mode
- Fast The analysis mode is fast but region borders may be less accurate.
- Slow The slow mode takes 6x longer to compute. Use when accurate region borders are needed.
- Add sub-region annotatons Add annotations for identified signal peptide sub-regions like n-region, h-region, c-region, cysteine, and twin-arginine motif.
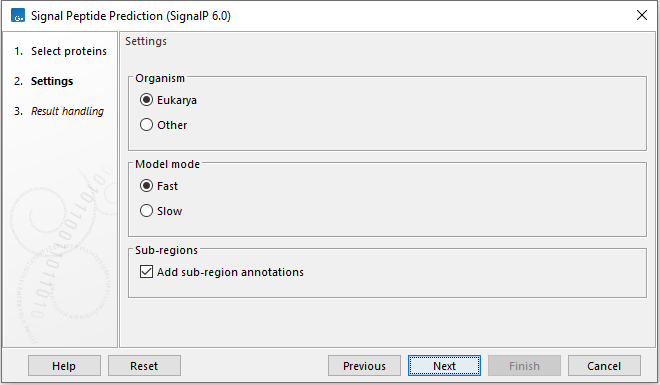
Figure 2.2: Set the options for SignalP 6.0.
In the Result handling wizard step, you specify the form the results should be returned in. The options are:
- Add annotations Annotate the input sequences with the signal peptides identified, and sub-regions if that option was selected earlier. See figure 2.3 for an example. Note: the option 'Signal peptide' must be checked in the Side Panel settings, in the 'Annotation layout' palette, for these annotations to be visible.
Working with sequence annotations is described in detail at https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcmainworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Working_with_annotations.html
- Create table Create a table containing an entry for each input sequence providing the likelihood of each type of signal peptide that was searched for See figure 2.4 for an example.
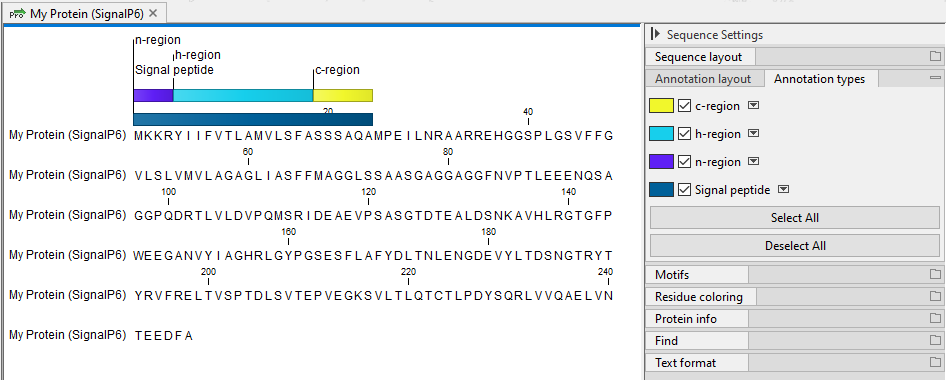
Figure 2.3: Sequence annotated with an identified signal peptide and sub-annotations providing information about individual sequence elements in the signal peptide, here c-, h- and n-regions.
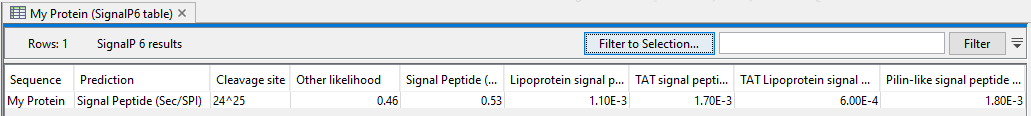
Figure 2.4: A table listing likelihood for each of the tested signal peptides.
Subsections
