Predict Cell Types
The Predict Cell Types tool uses a Cell Type Classifier (It can be found in the Toolbox here:
Cell Annotation (![]() ) | Predict Cell Types (
) | Predict Cell Types (![]() )
)
The following options can be adjusted (figure 7.1):
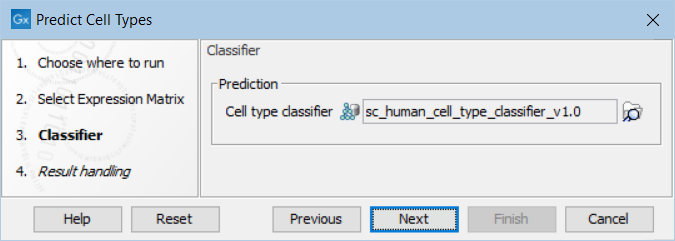
Figure 7.1: The options in the dialog of the Predict Cell Types tool. A Cell Type Classifier for human data downloaded from the Reference Data Manager has been selected.
- Cell type classifier. A classifier downloaded from the Reference Data Manager (see The Reference Data Manager) or produced by the Train Cell Type Classifier tool (see Train Cell Type Classifier). Note that the features in the input matrix and those used for training the classifier should be matching, see Features used for training and prediction.
The tool outputs:
- A Cell Clusters (
 ) object containing two categories:
) object containing two categories:
- "Cell type (all)" containing the predicted cell types, for each cell in the input matrix.
- "Cell type (high confidence)" containing the same predicted cell types, but with predictions with low probability being replaced with "Unknown". This can be useful for detecting novel cell types.
- Optionally, a Cell Annotations (
 ) object with the probabilities assigned for a subset of relevant cell types, for each cell in the input matrix. A cell type is considered relevant if:
) object with the probabilities assigned for a subset of relevant cell types, for each cell in the input matrix. A cell type is considered relevant if:
- The cell type is the predicted cell type for at least one cell in the "Cell type (all)" category, or
- There is at least one cell with a probability of at least
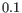 for the cell type.
for the cell type.
Using the outputs, the cells can be colored in a Dimensionality Reduction Plot (see Dimensionality reduction) by the predicted cell type (using the Cell Clusters) or the probability of having a specific cell type (using the Cell Annotations). Guided by the probabilities and other information, such as the clusters produced by the Cluster Single Cell Data tool (see Cluster Single Cell Data), the predicted cell types can be manually refined in the Dimensionality Reduction Plot (see Manual Annotation).
For details on how cell types are predicted, see SVMs for cell type classification.
