Running Detect Fusion Genes from DNA
To run the tool, go to:
Tools | Resequencing Analysis (![]() ) |
Variant Detection (
) |
Variant Detection (![]() ) | Detect Fusion Genes from DNA (
) | Detect Fusion Genes from DNA (![]() )
)
The tool takes as input a reads track (![]() ) containing mapped DNA reads.
) containing mapped DNA reads.
Selecting references
The following options can be configured in the References dialog (figure 31.53):
- Reference sequence. A sequence track (
 ) with the reference genome.
) with the reference genome.
The same track as used when mapping the DNA reads should be provided.
- Gene track. An annotation track (
 ) with the gene annotations.
) with the gene annotations.
- mRNA track. An optional annotation track (
 ) with the transcript annotations.
) with the transcript annotations.
- CDS track. An optional annotation track (
 ) with the coding sequence annotations.
) with the coding sequence annotations.
Optional annotation tracks do not impact fusion detection, but when provided, they add additional information to the outputs.
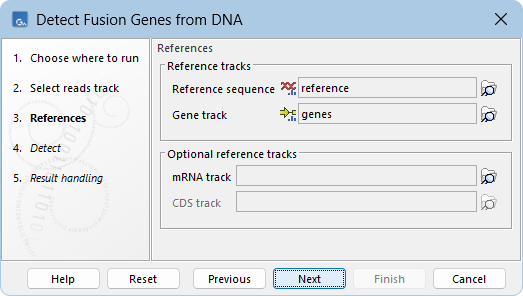
Figure 31.53: Reference tracks for Detect Fusion Genes from DNA
Detecting fusions
Fusion genes are detected by:
- Identifying unaligned ends from the input reads track.
- Mapping the unaligned ends to the reference genome.
- Determining potential fusions using the mapped unaligned ends, where each fusion is defined by breakpoint pairs connecting a 5' gene and a 3' gene.
See Fusion detection for details.
The following options can be configured in the Detect dialog (figure 31.54):
- Minimum length of unaligned ends. Only unaligned ends longer than this are used to detect fusions.
- Merge breakpoints within distance. Pairs of breakpoints of a fusion gene that are within this distance of each other are considered part of the same fusion event and are merged into a single breakpoint pair.
- Gene filter action. How detected fusions should be filtered based on the 5' and 3' genes. The following filter actions are available:
- None. Detected fusions are not filtered.
- Exclude. Detected fusions with a 5' or 3' gene in the provided track or list are removed. This can be useful for removing unwanted fusions.
- Include. Only detected fusions with a 5' or 3' gene in the provided track or list are kept. This can be useful for restricting fusion detection to only genes of interest.
The genes used for filtering can be provided using at least one of the following options:
- Genes for filtering (tracks). A gene track (
 ) that is a subset of the reference gene track. The gene IDs are used for filtering. Can be left empty or multiple tracks can be provided.
) that is a subset of the reference gene track. The gene IDs are used for filtering. Can be left empty or multiple tracks can be provided.
Several tracks suitable for excluding genes are available via the Reference Data Manager, see Exclude lists for details.
- Genes for filtering (names). A list of case-sensitive gene IDs or names separated by comma, semicolon, or any white-space character. Can be left empty.
Additionally, the following can be configured:
- Require both genes. When checked, both 5' and 3' genes must be in the provided track or list in order for the fusion to be filtered.
- Fusion filter action. How detected fusions should be filtered. The following filter actions are available:
- None. Detected fusions are not filtered.
- Exclude. Detected fusions in the provided table or list are removed. This can be useful for removing fusions that are frequently detected as false positives.
- Include. Only detected fusions in the provided table or list are kept. This can be useful for restricting fusion detection to only fusions of interest.
The fusions used for filtering can be provided using at least one of the following options:
- Fusions for filtering (tables). A table (
 ) with case-sensitive gene IDs or names. Can be left empty or multiple tables can be provided. The following formats are supported:
) with case-sensitive gene IDs or names. Can be left empty or multiple tables can be provided. The following formats are supported:
- The first two columns contain one gene each.
- The first column has a header with the word 'fusion' (case-insensitive) and contains gene pairs in the format 'gene1-gene2'.
- The first column has a header with the word 'genes' (case-insensitive) and contains a group of genes in the format 'gene1 gene2 gene3'. Each group results in all possible gene combinations, such as 'gene1-gene2', 'gene1-gene3', and 'gene2-gene3'.
All other columns are ignored.
See Standard import for details on how to import tables.
Several tables suitable for excluding fusions are available via the Reference Data Manager, see Exclude lists for details.
- Fusions for filtering (names). A list of case-sensitive gene IDs or names in the format 'gene1-gene2' separated by comma, semicolon, or any white-space character. Can be left empty.
If the IDs or names of genes in the fusions used for filtering contain a '-', the 'Fusions for filtering (tables)' using the second format ('fusion' header) and 'Fusions for filtering (names)' cannot be used. We recommend choosing one of the alternative options instead.
The fusions used for filtering are non-directional: a gene pair 'gene1-gene2' applies to fusions where gene1 is the 5' gene and gene2 is the 3' gene, as well as fusions where gene2 is the 5' gene and gene1 is the 3' gene.
- Assumed error rate. The probability of the binomial distribution used to calculate p-values. For example, an assumed error rate of 0.001 indicates that, on average, 1 in 1000 reads covering a breakpoint supports the fusion by chance.
The default value is deliberately conservative, which may impact detection of low-frequency fusions.
- Minimum number of supporting reads. The minimum number of reads that must support a fusion.
- Include all fusions in the track output. If checked, detected fusions that did not pass the configured filter options are included in the fusion track output. See Output from Detect Fusion Genes from DNA for details.
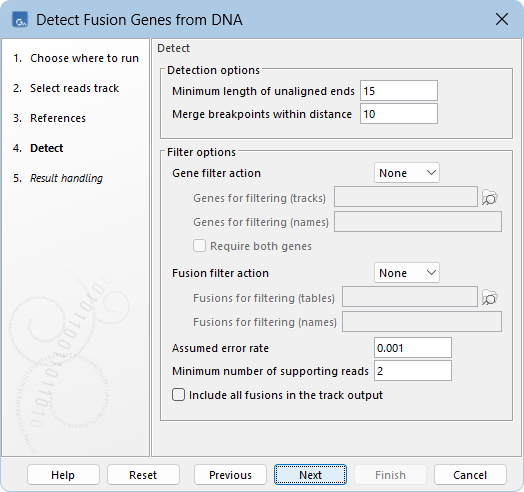
Figure 31.54: Default options for detecting and filtering fusion genes.
