Fusion detection
Fusion genes are detected by:
- Identifying unaligned ends from the input reads track.
- Mapping the unaligned ends to the reference genome using Map Reads to Reference with default options.
- Determining potential fusions using the mapped unaligned ends (figure 31.55).
- A potential fusion consists of a 5' and 3' gene and is defined by a pair of breakpoints.
- One breakpoint is at the position where the unaligned end begins.
- The other breakpoint is at the position where the unaligned end maps.
- The 5' breakpoint is the one where the breakpoint is towards the end of the gene.
- The 3' breakpoint is the one where the breakpoint is towards the beginning of the gene.
- For a given fusion gene, multiple fusions with distinct breakpoint pairs may be identified. Breakpoint pairs are merged according to Merge breakpoints within distance.
- Merging is done step by step. If breakpoint pair A can be merged with B, and B can be merged with C, then A, B, and C are all merged together.
- The position of the merged breakpoint pair is calculated as the median of the original breakpoints, with more weight given to breakpoint pairs supported by a higher number of reads.
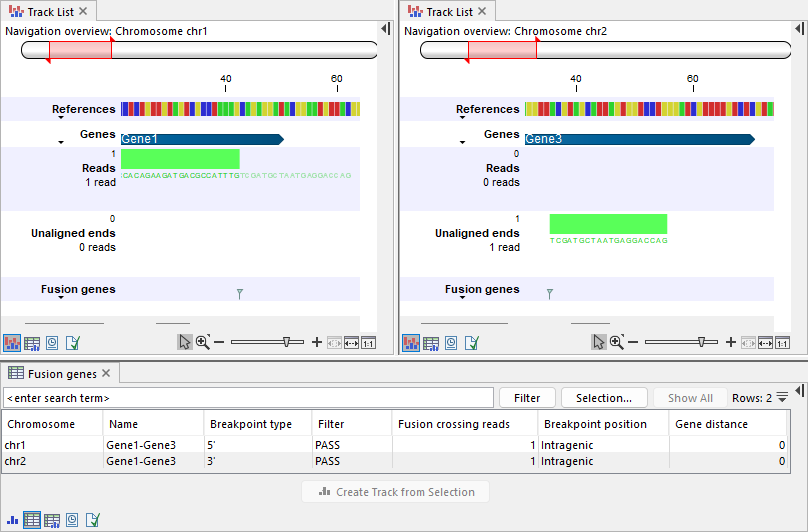
Figure 31.55: Top: Track lists showing the reference sequence, gene track, input reads track, output unaligned ends, and fusion genes track. Left: A read is mapped to Gene1 on chr1. Gene1 is annotated on the plus strand. The read is mapped in the forward direction (illustrated in green) and contains an unaligned end, resulting in a breakpoint at the 5' side. Right: The unaligned end maps to Gene3 on chr2. Gene3 is annotated on the plus strand and the unaligned end is mapped in the forward direction (illustrated in green). The corresponding breakpoint is at the 3' side, placed at the start of the mapped region, which corresponds to the beginning of Gene3. Bottom: Table view of the fusion genes track, showing the two breakpoints.
Whether a breakpoint is considered at the beginning or end of a gene depends on the gene's strand (figures 31.55 and 31.56).
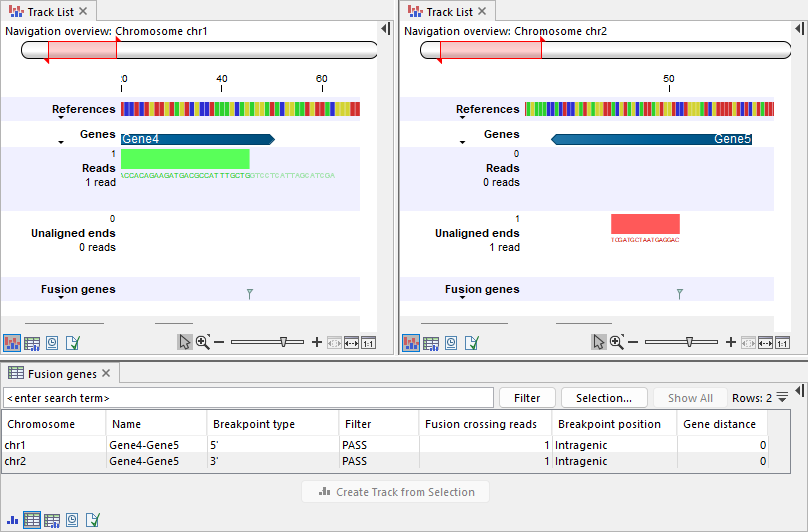
Figure 31.56: Top: Track lists showing the reference sequence, gene track, input reads track, output unaligned ends, and fusion genes track. Left: A read is mapped to Gene4 on chr1. Gene4 is annotated on the plus strand. The read is mapped in the forward direction (illustrated in green) and contains an unaligned end, resulting in a breakpoint at the 5' side. Right: The unaligned end maps to Gene5 on chr2. Gene5 is annotated on the minus strand and the unaligned end is mapped in the reverse direction (illustrated in red). The corresponding breakpoint is at the 3' side, placed at the end of the mapped region, which corresponds to the beginning of Gene5. Bottom: Table view of the fusion genes track, showing the two breakpoints.
Breakpoints can be located outside the gene, up to the the nearest gene along the same strand (figure 31.57):
- Breakpoints at the 5' side can be downstream of the gene, up to the start of the nearest gene.
- Breakpoints at the 3' side can be upstream of the gene, up to the end of the nearest gene.
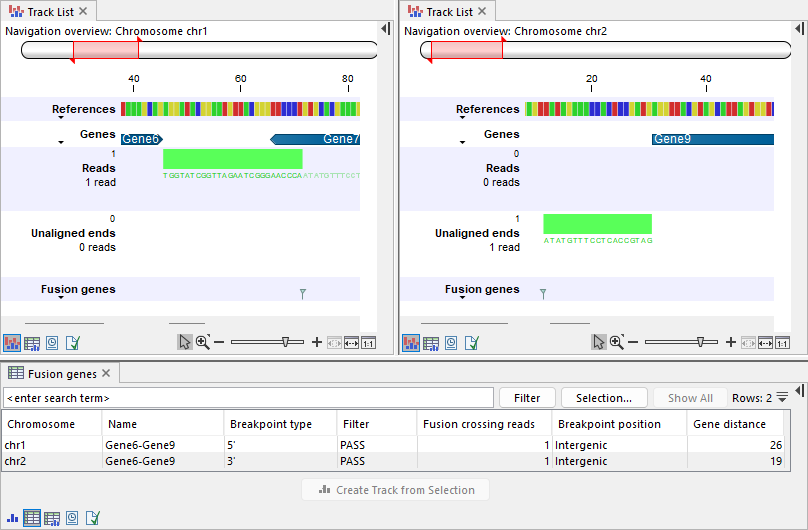
Figure 31.57: Top: Track lists showing the reference sequence, gene track, input reads track, output unaligned ends, and fusion genes track. Left: A read is mapped in the downstream region of Gene6. Gene6 is annotated on the plus strand. The read is mapped in the forward direction (illustrated in green) and contains an unaligned end, resulting in a breakpoint at the 5' side. Right: The unaligned end maps in the upstream region of Gene9 on chr2. Gene9 is annotated on the plus strand and the unaligned end is mapped in the forward direction (illustrated in green). The corresponding breakpoint is at the 3' side, placed at the start of the mapped region, which corresponds to the beginning of Gene9. Bottom: Table view of the fusion genes track, showing the two breakpoints with a non-zero 'Gene distance' and an intergenic 'Breakpoint position'.
The mapping direction of the read and its unaligned end can be on the same or opposite strand of the corresponding gene:
- Figures 31.55, 31.56, and 31.57 show examples where the read and unaligned end map on the same strand as the genes:
- Figure 31.58 shows genes annotated on the plus strand. The unaligned ends map in the opposite direction compared to both reads and the gene's strand. This is indicated in the 'Reversal' column.
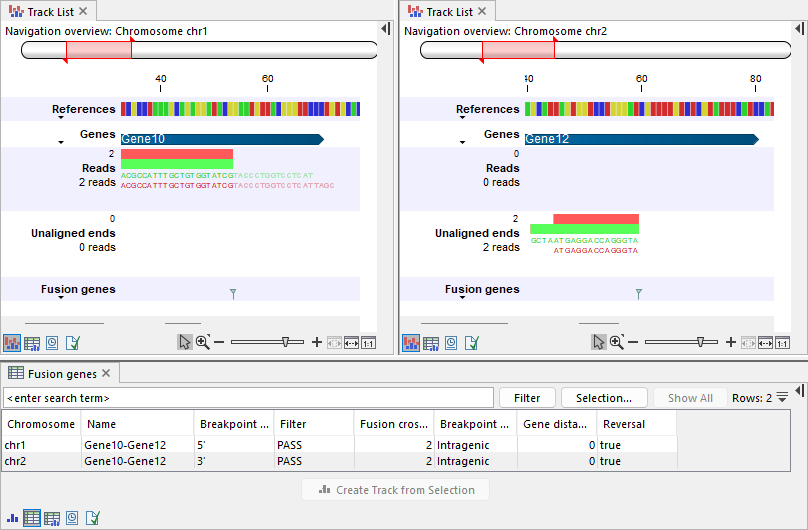
Figure 31.58: Top: Track lists showing the reference sequence, gene track, input reads track, output unaligned ends, and fusion genes track. Left: Two reads are mapped to Gene10 on chr1. Gene10 is annotated on the plus strand. The reads are mapped in the forward (illustrated in green) and reverse (illustrated in red) directions, respectively, and contain unaligned ends, resulting in a breakpoint at the 5' side. Right: The unaligned ends map to Gene12 on chr2. Gene12 is annotated on the plus strand and the unaligned ends are mapped in the reverse (illustrated in red) and forward (illustrated in green) directions, respectively. The corresponding breakpoint is at the 3' side, placed at the start of the mapped region, which corresponds to the beginning of Gene12. Bottom: Table view of the fusion genes track, showing the two breakpoints and that the reads changed strand orientation in 'Reversal'.
