Introduction
The CLC Server is the central part of CLC bio's enterprise solutions. You can see an overview of the server solution in figure 1.1).
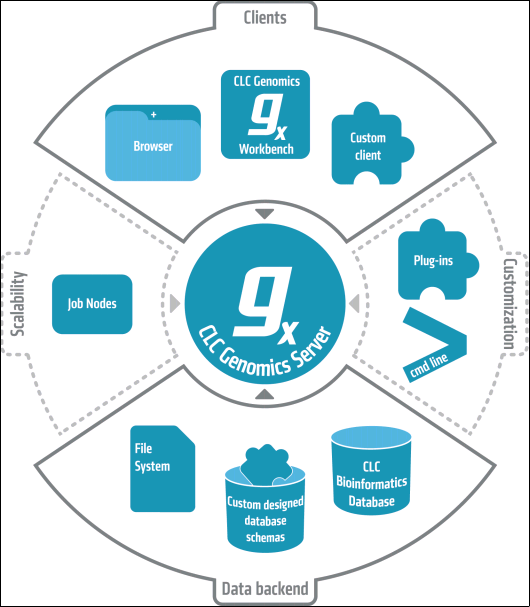
Figure 1.1: An overview of the server solution from CLC bio. Note that not all features are included with all license models.
The basic idea is that you can have the Server store data and run jobs centrally and thereby offload personal and typically smaller computers. For the user, the difference between working just with a Workbench and working with a Workbench and a server is very small. All the mechanisms for managing data, using the tools and visualizing the data are the same.
This user manual is intended to show how to take advantage of the server as a user. For information about administrating the server, please see the Administrator Manual.
The CLC Genomics Server is shipped with the following tools and analyses that can be started from the CLC Genomics Workbench or CLC Server Command Line Tools:
- Import
- Export
- Download Genome
- Alignments and Trees
- Create Alignment
- Create Tree
- Maximum Likelihood Phylogeny
- General Sequence Analysis
- Extract Annotations
- Extract Sequences
- Nucleotide Analysis
- Translate to Protein
- Convert DNA to RNA
- Convert RNA to DNA
- Reverse Complement Sequence
- Reverse Sequence
- Find Open Reading Frames
- Sequencing Data Analysis
- Trim Sequences
- Assemble Sequences
- Assemble Sequences to Reference
- Secondary Peak Calling
- Primers and Probes
- Find Binding Sites and Create Fragments
- BLAST
- BLAST
- BLAST at NCBI
- Download BLAST Databases
- Create BLAST Database
- Manage BLAST Databases
- NGS Core Tools
- Create Sequencing QC Report
- Merge Overlapping Pairs
- Trim Sequences
- Map Reads to Reference
- Local Realignment
- Create Detailed Mapping Report
- Merge Read Mappings
- Extract Consensus Sequence
- Process Tagged Sequences (Multiplexing)
- Track Tools
- Convert to Tracks
- Convert from Tracks
- Merge Annotation Tracks
- Annotate with Overlap Information (Annotate and Filter)
- Extract Reads Based on Overlap (Annotate and Filter)
- Filter Annotations on Name (Annotate and Filter)
- Filter Based on Overlap (Annotate and Filter)
- Create GC Contents Graph Tracks (Graphs)
- Create Mapping Graph Tracks (Graphs)
- Identify Graph Threshold Areas(Graphs)
- Resequencing Analysis
- Create Statistics for Target Regions
- Probabilistic Variant Detection
- Quality-based Variant Detection
- InDels and Structural Variants
- Coverage Analysis
- Annotate from Known Variants (Annotate and Filter Variants)
- Filter against Known Variants (Annotate and Filter Variants)
- Annotate with Exon Numbers (Annotate and Filter Variants)
- Annotate with Flanking Sequences (Annotate and Filter Variants)
- Filter Marginal Variant Calls (Annotate and Filter Variants)
- Filter Reference Variants (Annotate and Filter Variants)
- Compare Sample Variant Tracks (Compare Variants)
- Compare Variants within Group (Compare Variants)
- Fisher Exact Test (Compare Variants)
- Trio Analysis (Compare Variants)
- Filter against Control Reads (Compare Variants)
- GO Enrichment Analysis (Functional Consequences)
- Amino Acid Changes (Functional Consequences)
- Annotate with Conservation Score (Functional Consequences)
- Predict Splice Site Effect (Functional Consequences)
- Transcriptomics Analysis/ Expression Analysis
- RNA-Seq Analysis
- Extract and Count (Small RNA Analysis)
- Annotate and Merge Counts (Small RNA Analysis)
- Create Histogram (General Plots)
- Epigenomics Analysis
- ChIP-Seq Analysis
- De Novo Sequencing
- De Novo Assembly
- Map Reads to Contigs
The functionality of the CLC Genomics Server can be extended by installation of Server plugins. The available plugins can be found at http://www.clcbio.com/server_plugins.
