Mutate or repair amino acids
To mutate or repair an amino acid residue, right-click on any atom in the residue, and select "Mutate side chain" from the context menu (figure 10.23). A check-mark in the list of amino acids indicates the current amino acid type. If the amino acid is missing atoms, a repaired side chain will be created if the same amino acid type is selected from the list.
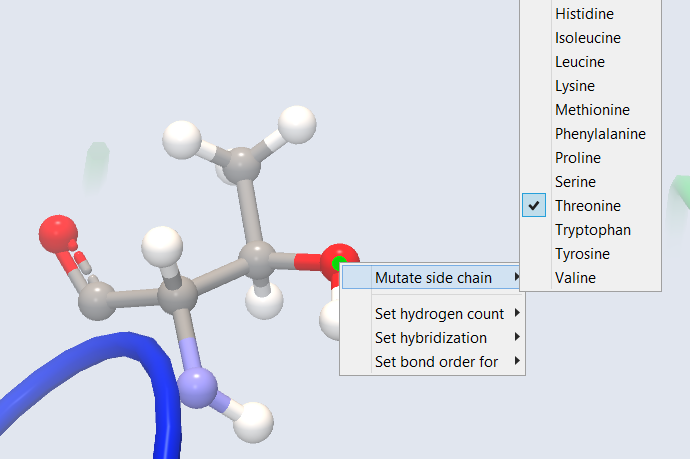
Figure 10.23: The right-click context menu on atoms in proteins has an option to mutate the current amino acid to another of the 20 standard amino acids.
A new protein chain with the mutated or repaired amino acid is added to the Project Tree. The original protein chain can either be kept or deleted from the Molecule Project (figure 10.24). Keep in mind that atom groups, Binding Site Setup and intermolecular bonds involving the original protein chain will be deleted if the original protein chain is deleted. The items that will be deleted together with the protein chain will always be specified in the dialog (see figure 10.24).
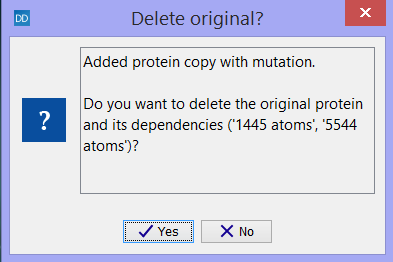
Figure 10.24: A new protein chain with the mutated or repaired amino acid is added to the Project Tree. The original protein chain can either be kept or deleted from the Molecule Project.
The atoms in the modeled residue will be assigned temperature values as described in Protein coloring to visualize local structural uncertainties. That means that atoms with steric clashes will be colored bright red when visualized using the "Color by Temperature" color scheme (Visualization styles and colors).
|
Please note
|
Subsections
