Analysis of sequencing data
You are now ready to perform the actual analysis of your sequencing data (see figure 4.13).
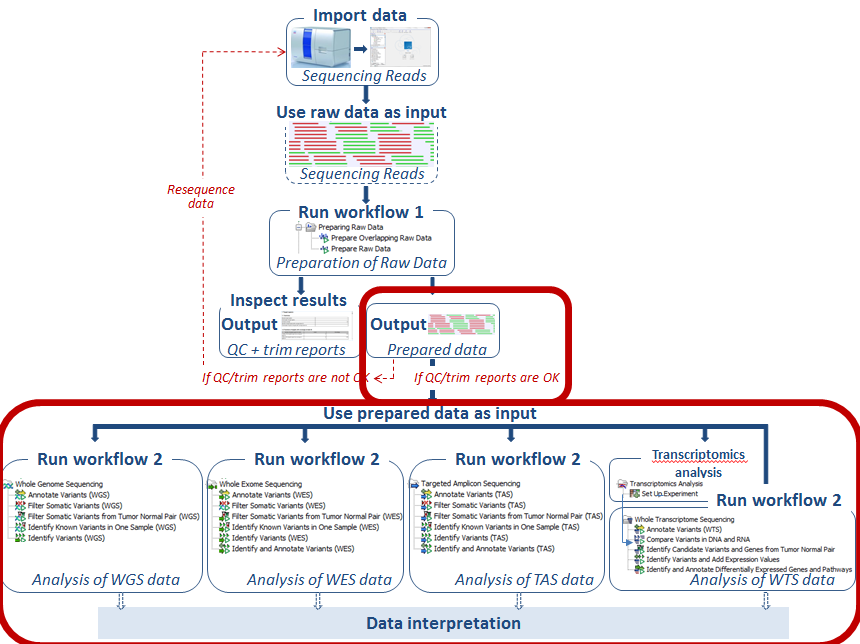
Figure 4.13: Use the prepared data as input in the relevant ready-to-use workflow, which we here for the sake of simplicity call "Workflow 2".
For each application six different ready-to-use workflows are available. These can be divided into three different categories; "Data analysis", "Interpretation", and "Data analysis and Interpretation".
Note! The ready-to-use workflows found under each of the three application types have similar names (with the only difference that "WGS", "WES", or "TAS" have been added after the name). However, some of the workflows have been tailored to the individual applications. Therefore, we recommend that you use the ready-to-use workflow that is found under the relevant application heading.
- Data analysis The data analysis includes read mapping and variant calling. One ready-to-use workflow is available in this category; the Identify Variants ready to use workflow.
- Interpretation At this step you can annotate, filter and compare the variants, that were identified in the data analysis step.
The available tools for interpretation are:
- Annotate Variants: Annotates variants with gene names, conservation scores, amino acid changes, and information from clinically relevant databases.
- Filter Somatic Variants: Removes variants outside the target region (only targeted experiments) and common variants present in publicly available databases. Annotates with gene names, conservation scores, and information from clinically relevant databases.
- Identify Somatic Variants from Tumor Normal Pair: Removes germline variants by referring to the control sample read mapping, removes variants outside the target region (in case of a targeted experiment), and annotates with gene names, conservation scores, amino acid changes, and information from clinically relevant databases.
- Data analysis and Interpretation With these ready-to-use workflows you can perform the variant calling, annotation, filtering, and/or comparison of variants in one go.
The available tools for Data analysis and Interpretation are:
- Identify and Annotate Variants: Maps reads to the human reference sequence, does a local realignment, runs quality control for targeted regions, calls variants, removes false positives, and annotates variants with gene names, amino acid changes, conservation scores, and information from different external databases.
- Identify Known Variants in One Sample: Maps sequencing reads and looks for the presence or absence of user-specified variants in the mapping.
