Import Large MLST Scheme
To run the Import Large MLST Scheme tool choose:
Microbial Genomics Module (![]() ) | Databases (
) | Databases (![]() ) | Large MLST (
) | Large MLST (![]() ) | Import Large MLST Scheme (
) | Import Large MLST Scheme (![]() )
)
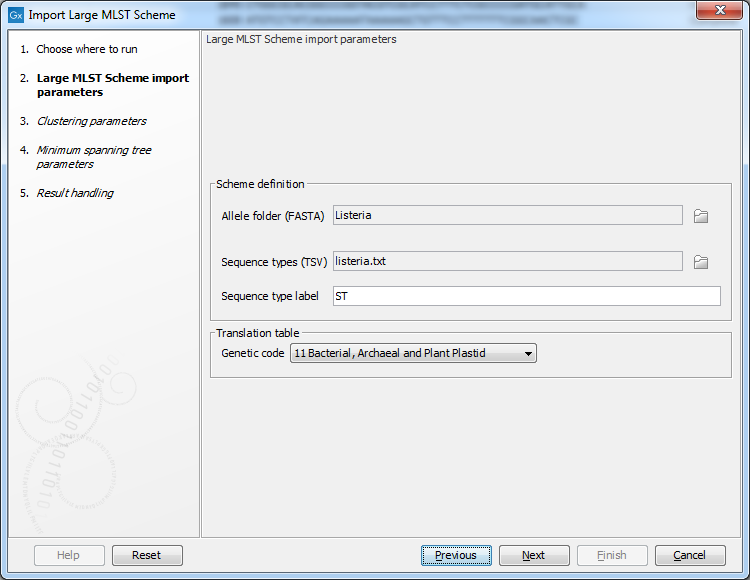
Figure 18.7: The Large MLST Scheme import parameters.
The Sequence types (TSV) file must be a tab-separated file listing a sequence type and its alleles in the following format:
ST pheS glyA fumC mdh sucA dnaN atpA clonal_complex 1 30 1 1 1 1 1 1 6 3 6 8 7 3 4 3 1 4 7 9 8 3 5 2 1 6 47 3 10 4 7 2 2It is possible to add arbitrary metadata as additional columns after the loci columns (e.g. the 'clonal_complex' column above)
The Allele folder (FASTA) must contain a set of FASTA files for each locus. The files must have one of the following extensions to be recognized: "fa", "fas", "fsa", "fasta", "tfa". The name of the allele must be the locus name and allele name separated by an underscore, like in this example:
>pheS_1 AGAGAAAAGAACGATACTTTCTATATGGCCCGTGATAATCAAGGCAAGCGTGTTGTCTTA >pheS_2 AGAGAAAAGAACGATACTTTCTATATGGCCCGTGATAATCAAGGCAAGCGTGTTGTCTTAThe clustering parameters and Minimum Spanning Tree parameters are similar to the options for the Create Large MLST Scheme tools.
The genetic code specified will be used for novel allele detection to make sure each allele starts and ends with an initiation and stop codon, respectively. If "No code specified" is selected, these requirements will not be checked when searching for novel alleles, instead the aligned part of the existing alleles to the assembly is used to define the allelic length. Note that the latter is useful for 7-gene MLST schemes which generally use fractions of genes, but it is also sensitive towards unaligned ends and may return too short alleles in some cases.
