Fastq to Annotated Germline Variants with Coverage Analysis
The Fastq to Annotated Germline Variants with Coverage Analysis template workflow:
- Identifies germline variants and annotates these with exon number and amino acid changes.
- Produces a read mapping.
- Reports coverage at target and gene level.
- Optionally identifies copy number variants (CNVs).
The workflow can only be used with targeted data.
The runtime of this workflow is significantly longer than the runtime of Fast to Annotated Germline Variants (Fastq to Annotated Germline Variants), because a read mapping track is saved.
Fastq to Annotated Germline Variants with Coverage Analysis can be found at:
Template Workflows | LightSpeed Workflows (![]() ) | Fastq to Annotated Germline Variants with Coverage Analysis (
) | Fastq to Annotated Germline Variants with Coverage Analysis (![]() )
)
If you are connected to a CLC Server via your Workbench, you will be asked where you would like to run the analysis. We recommend that you run the analysis on a CLC Server when possible.
In the first wizard step, select the target regions (figure 4.3).
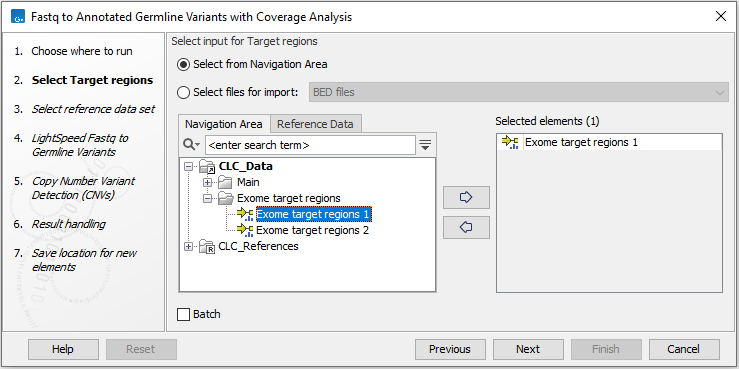
Figure 4.3: Select the target regions.
Next, select a Reference Data Set (figure 4.4). If you have not downloaded the Reference Data Set yet, the dialog will suggest the relevant data set and offer the opportunity to download it using the Download to Workbench button.
If none of the available reference data sets are appropriate, custom reference data sets can be created, see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Custom_Sets.html.
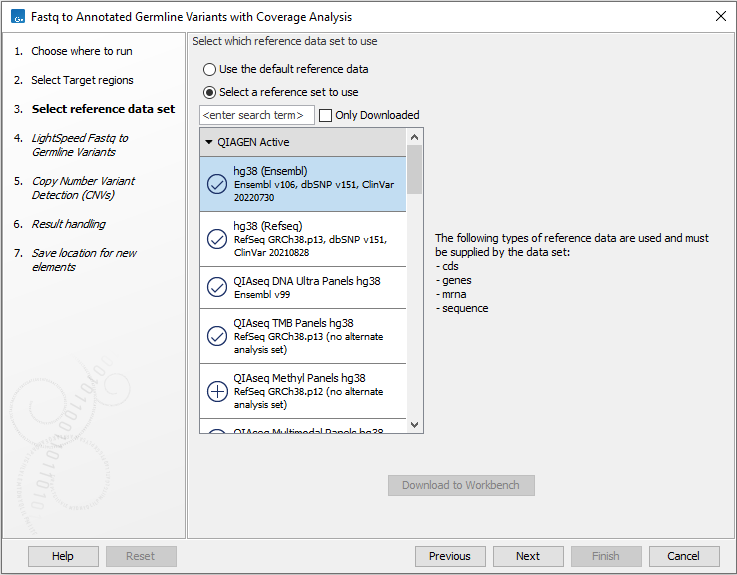
Figure 4.4: Select a reference data set.
In the LightSpeed Fastq to Germline Variants wizard step (figure 4.5) you have the following options:
- Reads (fastq) Press Browse to select fastq files for analysis.
- Masking mode To enable reference masking when mapping reads, set this option and select a masking track.
- Masking track Provide a masking track for the chosen reference genome if reference masking has been enabled.
- Discard duplicate mapped reads Duplicate mapped reads are per default replaced with a consensus read. Untick if duplicate mapped reads should be retained. See Deduplication for additional details.
- Lenient inversion detection Enable lenient inversion detection to allow detection of inversions which only has read support in one direction on each of the breakpoints. This is recommended for targeted data. Enabling this option can increase processing time and can result in detection of more false positive inversions.
- Batch Select if fastq files from different samples are used as input, and each sample should be analyzed individually. The names of the fastq files must follow standard Illumina naming scheme to allow the tool to identify individual fastq files as belonging to the same sample.
- Join lanes when batching Select to join fastq files from the same sample that were sequenced on different lanes.
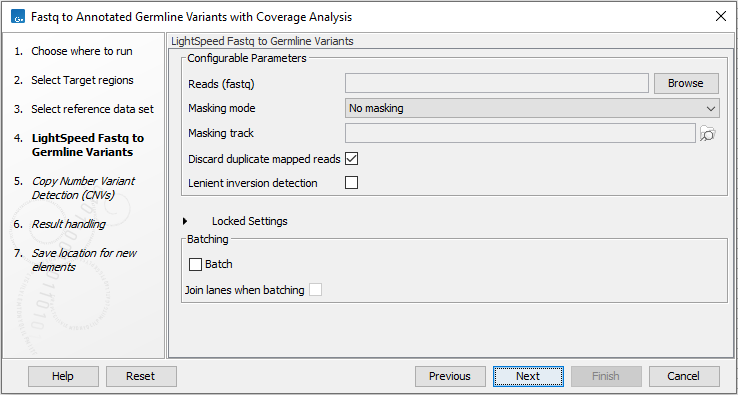
Figure 4.5: Select fastq files.
In the wizard step Copy Number Variant Detection (CNVs), it is possible to specify control coverage tables or read mappings for copy number variant detection (figure 4.6). If controls are not provided, copy number variant detection will not be performed. Read about copy number variant detection here http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Copy_Number_Variant_Detection.html.
Note that for CNV detection it is important that the same processing is applied to control samples and the sample that is tested for CNVs. We recommend using the LightSpeed template workflow Fastq to Germline CNV Control tro create appropriate control coverage tables, see Fastq to CNV Control.
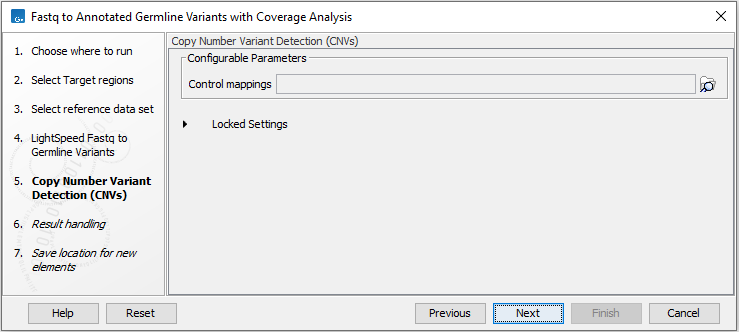
Figure 4.6: Select control coverage tables or read mappings for copy number variant detection.
In the final wizard step, choose to Save the results of the workflow and specify a location in the Navigation Area before clicking Finish.
Subsections
