Allele table
The allele table displays all Genotype track alleles, one variant per row, and the displayed columns are allele variant and haplotype allele annotations as default. Variants where filters apply are displayed when the option 'Show filtered' is enabled. Blue columns are sample specific annotations, corresponding to FORMAT annotations in VCF (figure 10.4).
Below are descriptions of general allele table annotations. Common allele table annotations created by a specific tool can be found here: Microhaplotype Caller - Annotations
- Chromosome
- The name of the reference sequence where the allele is situated.
- Region
- The reference sequence positions of the locus. The region may be either a 'single position', a 'region' or a 'between position region'.
- Type
- Allele variants are classified into five different types:
- SNV. A single nucleotide variant. This is also often referred to as a SNP.
- MNV. A multi nucleotide variant, which has the same number of nucleotides as the reference allele.
- Insertion. A variant that solely differs from the reference by having one or more adjacent bases inserted. The reference allele in a locus with zero length is called a reference insertion and also has type Insertion.
- Deletion. A variant that solely differs from the reference by having one or more adjacent bases deleted.
- Replacement. A variant that differs from the reference by length, and by having one or more bases replaced by one or more bases. This is also referred to as a delins. An example could be
AAA->CC.
- Reference
- The reference allele nucleotide sequence of the locus. Maximally 20 nucleotides are shown. Longer sequences can be obtained in their entirety by copy-pasting the table cell.
- Allele
- The allele. Nucleotide sequence is shown if this is a simple small variant.
- Reference allele
- Describes whether the allele is identical to the reference with a 'Yes' or 'No'. This can be useful for table filtering and sorting.
- Alteration Length
- Maximum length of the allele and the reference allele.
- Filter'
- List of filters that are directly or indirectly applicable to the allele variant. The value 'PASS' specifies that the variant passed all filters.
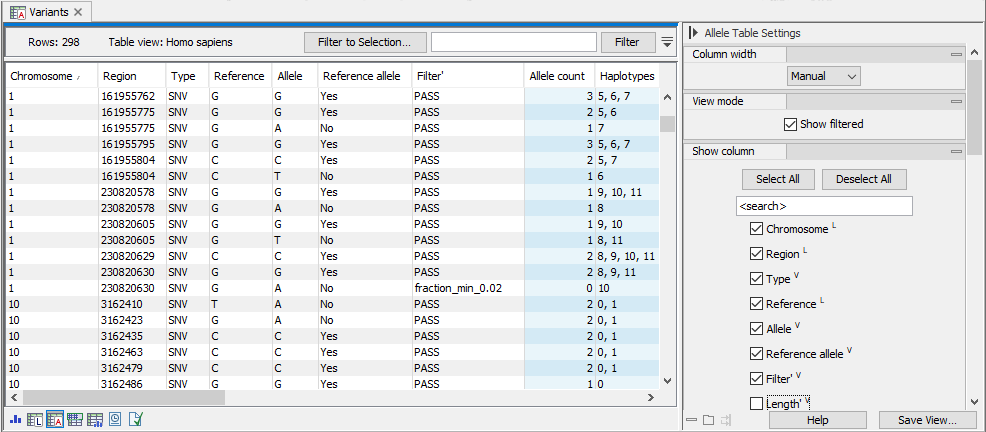
Figure 10.4: The allele table. To go to the allele table view of a genotype track as shown here, select the table icon with an A in the lower left corner. Note that in this example, "Show filtered" has been checked in the side panel and a filtered locus is shown in the bottom half of the table. Columns displayed can be adjusted by selecting and deselecting columns in the side panel to the right.
Sample annotations
The following annotations are available in sample Genotype tracks.
- Allele count
- Count of alleles at this locus, identical to this allele variant. Based on separation of haplotypes the variant is part of, as well as the number of haplotype copies (figure 10.4).
- Haplotypes
- Haplotype identifiers. All sample alleles are part of one or more haplotypes. Haplotypes are groups of phased alleles that are linked together in the same DNA molecule. An allele may be part of multiple haplotypes describing different aspects of the same DNA molecule (figure 10.4).
- Locus number
- Haplotype locus number. The number of loci this haplotype spans, including filtered.
- Separation
- Haplotype separation. Identifiers of all incompatible haplotypes, listed for each haplotype and in the same order. Two haplotypes are incompatible if they are separated by having different alleles at any position. Any enforced separation is included, whereas single locus haplotypes are not included (unless enforced).
- Enforced separation
- Enforced haplotype separation. Identifiers of separated haplotypes, listed for each haplotype and in the same order. Haplotype separation may be enforced based on knowledge about haplotype incompatibility in parts of the chromosome that are not included in the Genotype track, for example when a homozygous locus that is part of two separated haplotypes is extracted using 'Create Track from Selection'.
- Copies
- Number of identical allelic copies represented by a haplotype. Listed for each haplotype and in the same order. Defaults to one and includes any additional enforced copies.
- Enforced copies
- Enforced haplotype copies. Number of additional identical allelic copies represented by a haplotype. Listed for each haplotype and in the same order. Haplotype copies can for example be enforced based on an expected ploidy.
- Haplotype allele filter
- Applicable haplotype allele specific filters.
- Overlap allele
- Presence of this annotation indicates that this is an overlap allele,
meaning that parts of the allele sequence at this locus are described by alleles at overlapping loci,
and that the allele sequence at this locus may be unavailable.
The annotation value '
<NS>' indicates that the haplotype allele sequence at this locus is not available and must be derived from other loci in the complex region. The haplotype allele is in that case represented as the overlap variant specified by the track complex representation.When the sequence is available for this overlap allele, then the annotation value specifies the actual haplotype allele sequence. The overlap allele can in that case either be represented as the proper allele variant with actual sequence, or as the overlap variant specified by the track complex representation.
Note that when the overlap allele is represented as the overlap variant, the actual haplotype allele sequence may differ from that of the variant it is represented as.
While specification of overlap allele sequence may be considered redundant, other allele annotations can provide locus specific information that is not.
In Track view, overlap alleles are only shown in 'Allele count'-mode, and only when the actual sequence is available.
