Identify Somatic Variants from Tumor Normal Pair (WES)
The Identify Somatic Variants from Tumor Normal Pair (WES) ready-to-use workflow can be used to identify potential somatic variants in a tumor sample when you also have a normal/control sample from the same individual.
When running this workflow the reads are mapped and the variants identified. An internal workflow removes germline variants that are found in the mapped reads of the normal/control sample and variants outside the target region are removed as they are likely to be false positives due to non-specific mapping of sequencing reads. Next, remaining variants are annotated with gene names, amino acid changes, conservation scores and information from relevant databases like ClinVar (variants with clinically relevant association). Finally, information from dbSNP is added to see which of the detected variants have been observed before and which are completely new.
Before starting the workflow, you will need to import in the workbench a file with the genomic regions targeted by the amplicon or hybridization kit. Such a file (a BED or GFF file) is usually available from the vendor of the enrichment kit and sequencing machine. Use the Import | Tracks tool to import it in your Navigation Area.
Run the Identify Somatic Variants from Tumor Normal Pair (WES) workflow
To run the Identify Somatic Variants from Tumor Normal Pair (WES) tool, go to:
Toolbox | Ready-to-Use Workflows | Whole Exome Sequencing (![]() ) | Somatic Cancer (
) | Somatic Cancer (![]() ) | Identify Somatic Variants from Tumor Normal Pair (WES) (
) | Identify Somatic Variants from Tumor Normal Pair (WES) (![]() )
)
- Go to the toolbox and double-click on the Identify Somatic Variants from Tumor Normal Pair (WES) ready-to-use workflow.
- First (figure 21.24), select the tumor sample reads.
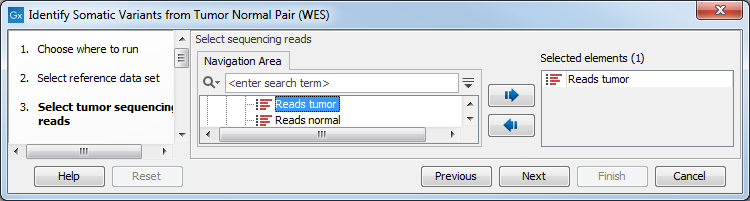
Figure 21.24: Select the tumor sample reads. - In the next wizard step, specify the normal sample reads.
- In the next dialog, select which data set should be used to identify variants (figure 21.25).
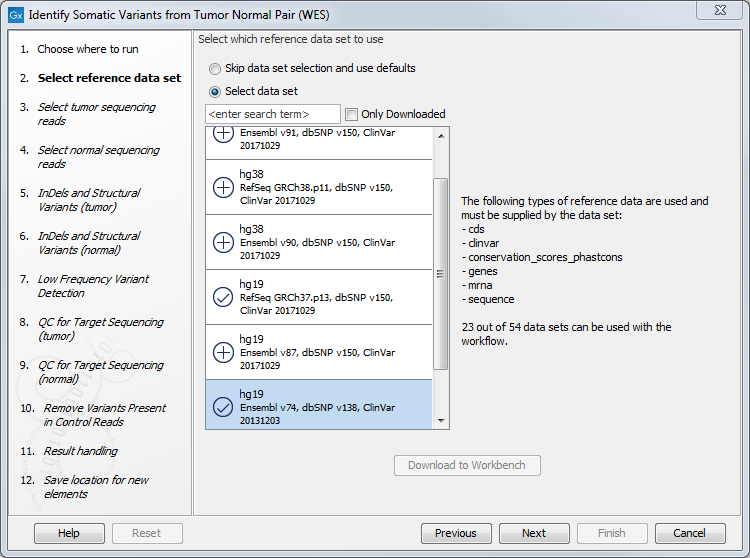
Figure 21.25: Choose the relevant reference Data Set to identify variants. - The following 2 steps allow you to restrict the calling of Indels and Structural Variants to the targeted regions, both for tumor and normal reads (figure 21.26).
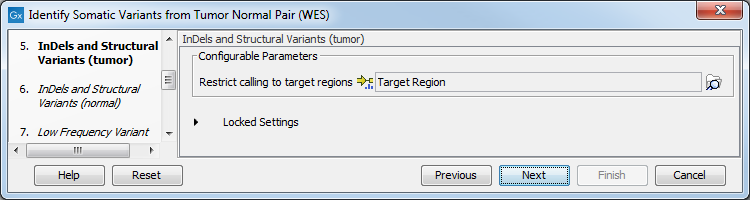
Figure 21.26: Specify the target regions track. - Set the parameters for the Low Frequency Variant Detection step (figure 21.27).
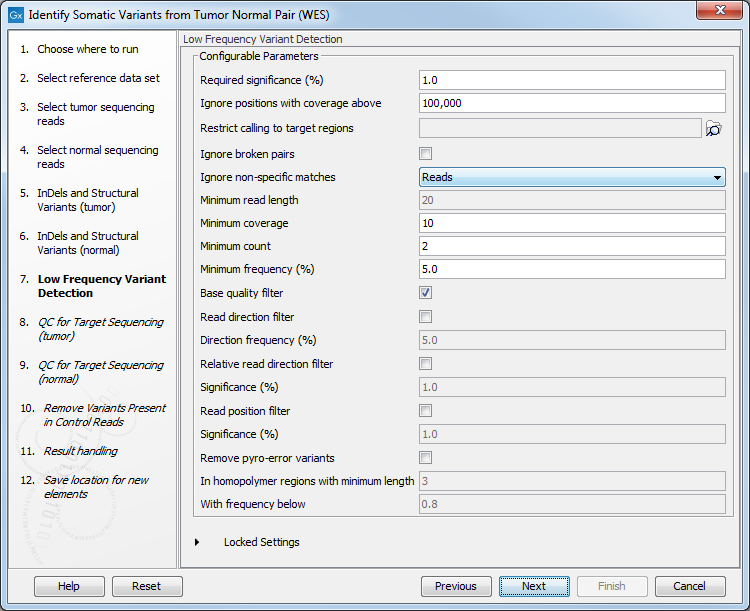
Figure 21.27: Specify the settings for the variant detection.For a description of the different parameters that can be adjusted, see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Low_Frequency_Variant_Detection.html. If you click on "Locked Settings", you will be able to see all parameters used for variant detection in the ready-to-use workflow.
- In the following 2 wizard steps, you can select your target regions track to be used for reporting the performance of the targeted re-sequencing experiment for the tumor and normal samples successively (figure 21.28). The targeted region track should be the same as the track you selected in the previous wizard steps. Variants found outside the targeted regions will not be included in the output that is generated with the ready-to-use workflow.
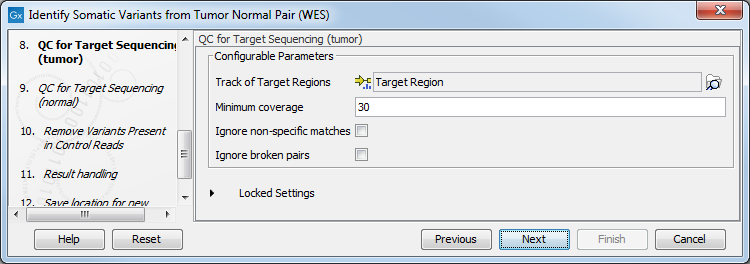
Figure 21.28: Select your target region track.For a description of the different parameters that can be adjusted, see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=QC_Targeted_Sequencing.html. If you click on "Locked Settings", you will be able to see all parameters used for the QC for Targeted Sequencing tool in the ready-to-use workflow.
- In the Remove Variants Present in Control Reads step, you can adjust the settings for removal of germline variants (figure 21.29).
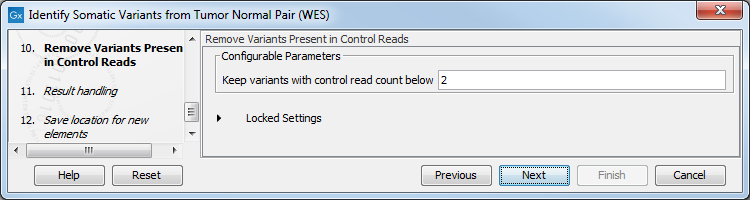
Figure 21.29: Specify setting for removal of germline variants. - In the last wizard step you can check the selected settings by clicking on the button labeled Preview All Parameters.
In the Preview All Parameters wizard you can only check the settings, and if you wish to make changes you have to use the Previous button from the wizard to edit parameters in the relevant windows.
- Choose to Save your results and click Finish.
Output from the Identify Somatic Variants from Tumor Normal Pair (WES) workflow
The following outputs are generated:
- Read Mapping Normal (
 ) The mapped sequencing reads for the normal sample. The reads are shown in different colors depending on their orientation, whether they are single reads or paired reads, and whether they map unambiguously (see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Coloring_mapped_reads.html).
) The mapped sequencing reads for the normal sample. The reads are shown in different colors depending on their orientation, whether they are single reads or paired reads, and whether they map unambiguously (see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Coloring_mapped_reads.html).
- Read Mapping Tumor (
 ) The mapped sequencing reads for the tumor sample.
) The mapped sequencing reads for the tumor sample.
- Target Region Coverage Report Normal (
 ) The report consists of a number of tables and graphs that in different ways provide information about the mapped reads from the normal sample.
) The report consists of a number of tables and graphs that in different ways provide information about the mapped reads from the normal sample.
- Target Region Coverage Tumor (
 ) A track showing the targeted regions. The table view provides information about the targeted regions such as target region length, coverage, regions without coverage, and GC content.
) A track showing the targeted regions. The table view provides information about the targeted regions such as target region length, coverage, regions without coverage, and GC content.
- Target Region Coverage Report Tumor (
 ) The report consists of a number of tables and graphs that in different ways provide information about the mapped reads from the tumor sample.
) The report consists of a number of tables and graphs that in different ways provide information about the mapped reads from the tumor sample.
- Amino Acids Changes Track that shows the consequences of the variants at the amino acid level in the context of the original amino acid sequence. A variant introducing a stop mutation is illustrated with a red amino acid.
- Annotated Somatic Variants (
 ) A variant track holding the identified and annotated somatic variants. The variants can be shown in track format or in table format. When holding the mouse over the detected variants in the Track List, a tooltip appears with information about the individual variants. You will have to zoom in on the variants to be able to see the detailed tooltip.
) A variant track holding the identified and annotated somatic variants. The variants can be shown in track format or in table format. When holding the mouse over the detected variants in the Track List, a tooltip appears with information about the individual variants. You will have to zoom in on the variants to be able to see the detailed tooltip.
- Track List Tumor Normal Comparison (
 ) A collection of tracks presented together. Shows the annotated variant track together with the human reference sequence, genes, transcripts, coding regions, the mapped reads for both normal and tumor, the annotated somatic variants, information from the ClinVar database, and finally a track showing the conservation score (see figure 21.30).
) A collection of tracks presented together. Shows the annotated variant track together with the human reference sequence, genes, transcripts, coding regions, the mapped reads for both normal and tumor, the annotated somatic variants, information from the ClinVar database, and finally a track showing the conservation score (see figure 21.30).
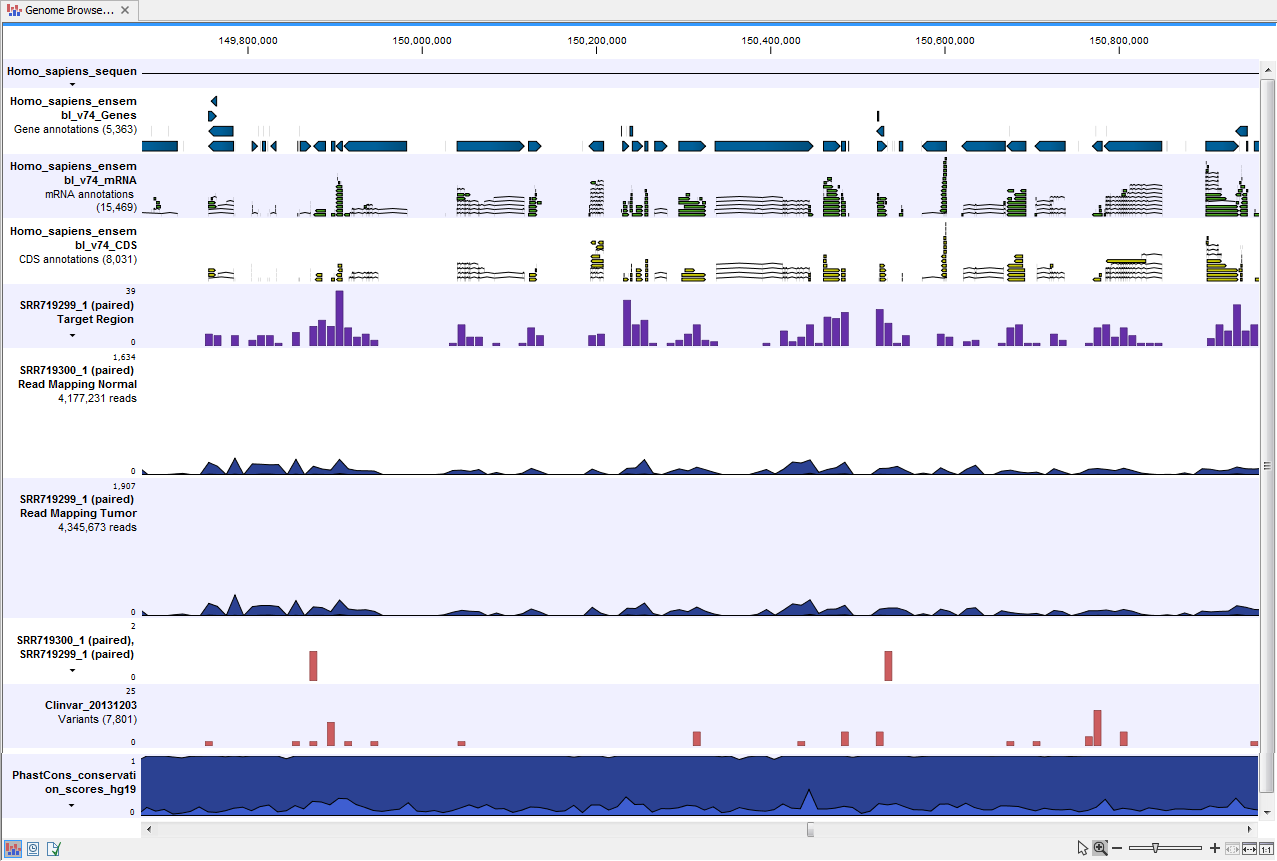
Figure 21.30: The Track List presents all the different data tracks together and makes it easy to compare different tracks.
