MGI/BGI
The MGI/BGI importer is designed to import fastq (.fastq/.fq) files generated by MGI/BGI sequencing technology. Uncompressed files as well as files compressed using gzip (.gz), zip (.zip) or bzip2 (.bz2) can be provided as input. Quality scores are expected to be in the NCBI/Sanger format, see Quality scores in the Illumina platform. The importer processes UMI information from the fastq read headers, see General notes on UMIs.
To launch the MGI/BGI importer, go to:
Import (![]() ) | Other NGS Reads (
) | Other NGS Reads (![]() ) | MGI/BGI (
) | MGI/BGI (![]() ).
).
This opens a dialog where files can be selected and import options specified (figure 7.14).
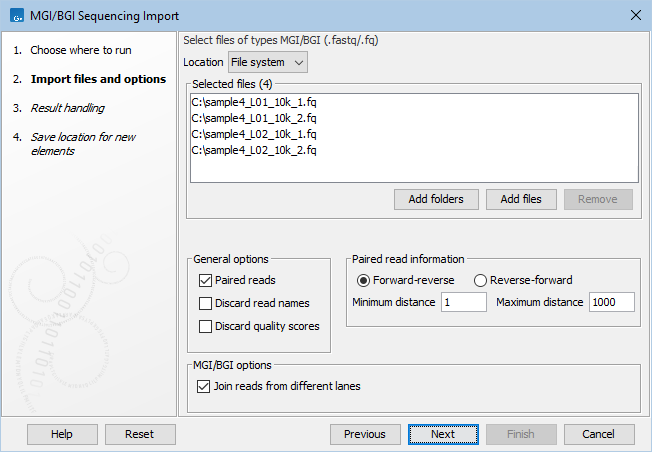
Figure 7.14: Importing data from MGI/BGI.
The General options are:
- Paired reads. Files will be paired up based on their names, which are assumed to end with _1 and _2, respectively. If this is not the case, files will be paired up based on the names of their first read, using one of the following formats:
- The read names end with /1 and /2, for example
@sample1/1and@sample1/2. - The read names contain a space followed by 1 or 2, for example
@sample1 1:NNNand@sample1 2:NNN.
Under Paired read information:
- Choose the orientation of the paired reads, either Forward-reverse or Reverse-forward.
- Specify the insert sizes by setting Minimum distance and Maximum distance. Data sets with different insert sizes should be imported separately, with the correct minimum and maximum distance.
Read more about handling paired data in General notes on handling paired data.
- The read names end with /1 and /2, for example
- Discard read names. Read names can be discarded to save disk space without affecting analysis results. Keeping read names can be useful in some circumstances, such as when inspecting sequence list contents or when working downstream with subsets of sequences.
- Discard quality scores. Quality scores are visible in read mappings and are used by various tools, e.g. for variant detection. If quality scores are not relevant, use this option to discard them and reduce disk space and memory consumption.
The MGI/BGI options are:
- Join reads from different lanes. The CLC Genomics Workbench will group files based on their name and import reads from different lanes into the same sequence list. The lane is identified in the file name in the form
L<at least one digit>. E.g.,MySample_L01_10k_1.fqMySample_L01_10k_2.fqMySample_L02_10k_1.fqMySample_L02_10k_2.fq
