Extract Reads
This tool can be used to extract reads from read mappings. To launch the tool, go to:
Toolbox | Utility Tools (![]() ) | Extract Reads (
) | Extract Reads (![]() )
)
Read mapping tracks can be used as input (figure 34.13).
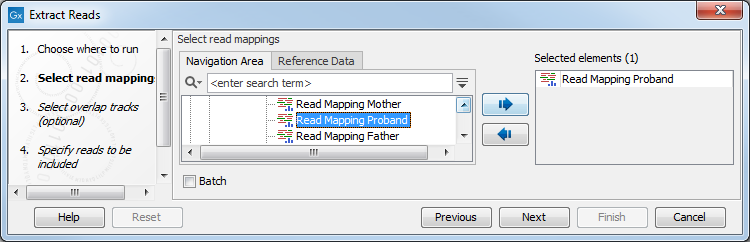
Figure 34.13: Select a read mapping. Only one read mapping can be selected at the time.
The next step allows reads to be extracted based on their mapped genomic position (figure 34.14). If an Overlap track is supplied then only reads overlapping the elements in the track are extracted. If no Overlap track is supplied then all reads are extracted at this step. Note that it is also possible to select here an RNA-seq statistical comparison.
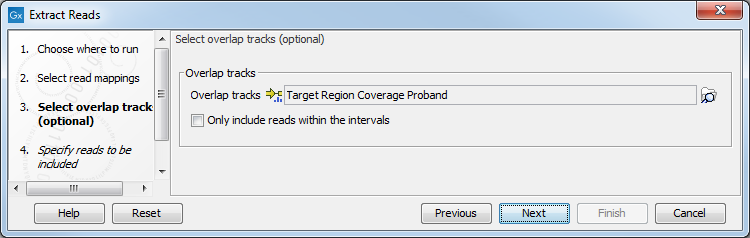
Figure 34.14: Select the track(s) containing the annotation(s) of interest. Multiple tracks can be selected at the same time.
With the options "Only include reads within the intervals", it is possible to choose whether only reads within the intervals should be extracted, or whether reads continuing outside the annotated region should be extracted. The difference between the options can be seen in figure 34.15.
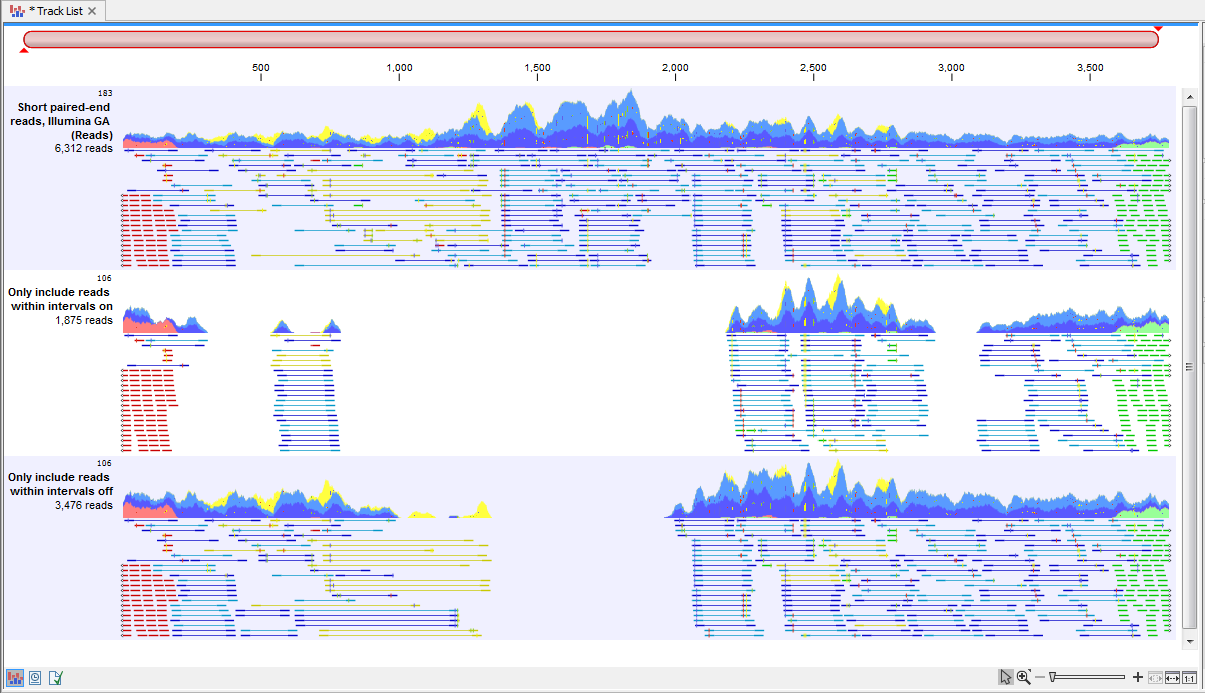
Figure 34.15: Output from the Extract Reads tool. Top: The read mapping used as input. Middle: Output when "Only include reads within intervals" has been selected. Bottom: Output when "Only include reads within intervals" has been deselected.
In the next dialog, specify which reads should be included in the output. They are all selected by default as seen in figure 34.16.
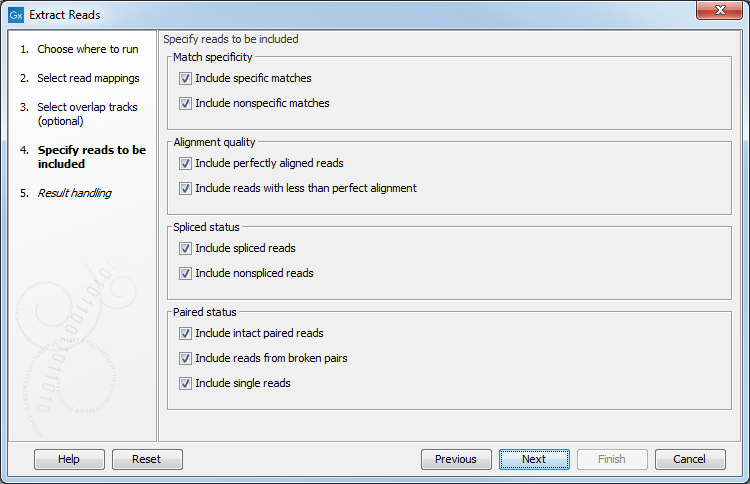
Figure 34.16: Options to include or exclude specific types of reads from the output.
- Match specificity
- Include specific matches Reads that only are mapped to one position.
- Include non-specific matches Reads that have multiple equally good alignments to the reference. These reads are colored yellow per default.
- Alignment quality
- Include perfectly aligned reads Reads where the full read is perfectly aligned to the reference sequence (or consensus sequence for de novo assemblies). Note that at the end of the contig, reads may extend beyond the contig (this is not visible unless you make a selection on the read and observe the position numbering in the status bar). Such reads are not considered perfectly aligned reads because they do not align in their entire length.
- Include reads with less than perfect alignment Reads with mismatches, insertions or deletions, or with unaligned nucleotides at the ends (the faded part of a read).
- Spliced status
- Include spliced reads Reads that are mapped across an intron.
- Include non spliced reads Reads that are not mapped across an intron.
- Paired status
- Include intact paired reads Paired reads that are mapped within the paired distance specified. Per default, these reads are colored blue.
- Include reads from broken pairs Paired reads where only one of the reads is mapped either because only one read in the pair matches, or because the distance or relative orientation is wrong. The reads are colored as single reads.
- Include single reads This includes reads that are marked as single reads (as opposed to paired reads). Note that paired reads that have been broken during assembly are not included in this category. Single reads that come from trimming paired sequence lists are included in this category.
In the last step, you can choose to output a reads track or sequence list(s).
