Assemble sequences
This section describes how to assemble a number of sequence reads
into a contig without the use of a reference sequence (a known
sequence that can be used for comparison with the other sequences,
see Assemble to reference
sequence). To perform the assembly:
Toolbox | Sequencing Data Analysis ( )|
Assemble Sequences (
)|
Assemble Sequences ( )
)
This will open a dialog where you can select sequences to assemble. If you already selected sequences in the Navigation Area, these will be shown in 'Selected Elements'. You can alter your choice of sequences
to assemble, or add others, by using the arrows to move sequences between the Navigation Area and the 'Selected Elements' box. You can also add sequence lists.
Note! You can assemble a maximum of 2000 sequences at a time.
To assemble more sequences, please use the De Novo Assembly ( ) tool under De Novo Sequencing (
) tool under De Novo Sequencing ( ) in the Toolbox instead.
) in the Toolbox instead.
To assemble more sequences, you need the CLC Genomics Workbench (see http://www.clcbio.com/genomics).
When the sequences are selected, click Next. This will show the
dialog in figure 31.6
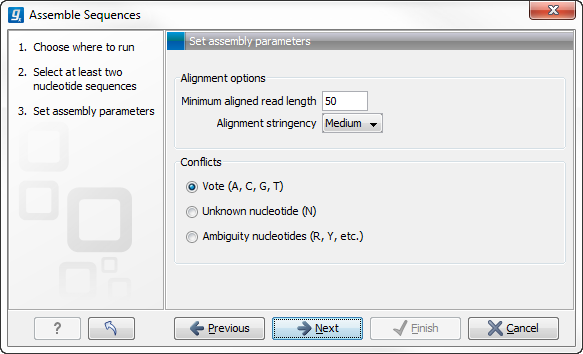
Figure 31.6: Setting assembly parameters.
This dialog gives you the following options for assembly:
- Minimum aligned read length. The minimum number of nucleotides in a read which must be successfully aligned
to the contig. If this criteria is not met by a read, the read is
excluded from the assembly.
- Alignment stringency. Specifies the stringency of the scoring function used by the alignment step in the contig
assembly algorithm. A higher stringency level will tend to produce
contigs with fewer ambiguities but will also tend to omit more
sequencing reads and to generate more and shorter contigs. Three
stringency levels can be set:
- Conflicts. If there is a conflict, i.e. a position where there is disagreement about the residue (A, C, T or G), you can specify how the contig sequence should reflect the conflict:
- Vote (A, C, G, T). The conflict will be solved by counting instances of each nucleotide
and then letting the majority decide the nucleotide in the contig. In case of equality, ACGT are given priority over one another in the stated order.
- Unknown nucleotide (N). The contig will be assigned an 'N' character in all positions with conflicts (conflicts are registered already when two nucleotides differ).
- Ambiguity nucleotides (R, Y, etc.). The contig will display an ambiguity nucleotide reflecting the different nucleotides found in the reads (nucleotide ambiguity is registered already when two nucleotides differ).
For an overview of ambiguity codes, see IUPAC codes for
nucleotides.
Note, that conflicts will always be highlighted no matter
which of the options you choose. Furthermore, each conflict
will be marked as annotation on the contig sequence and will be present if the contig sequence is extracted for further analysis.
As a result, the details of any experimental heterogeneity can be maintained and used when the result of single-sequence analyzes
is interpreted. Read more about conflicts.
- Create full contigs, including trace data. This will create a contig where all the aligned reads
are displayed below the contig sequence. (You can always extract
the contig sequence without the reads later on.) For more
information on how to use the contigs that are created, see
View and
edit contigs.
- Show tabular view of contigs. A contig can be shown both in a graphical as well as a tabular view.
If you select this option, a tabular view of the contig will also be
opened (Even if you do not select this option, you can show the
tabular view of the contig later on by clicking
Table (
 ) at the bottom of the view.) For more
information about the tabular view of contigs, see
Assembly variance
table.
) at the bottom of the view.) For more
information about the tabular view of contigs, see
Assembly variance
table.
- Create only consensus sequences. This will not display a contig but will only output the assembled contig sequences
as single nucleotide sequences. If you choose this option it is not possible to validate the assembly process and edit the contig based on the traces.
Click Next if you wish to adjust how to
handle the results. If not, click Finish.
When the assembly process has ended, a number of views will be
shown, each containing a contig of two or more sequences that have
been matched. If the number of contigs seem too high or low, try
again with another Alignment stringency setting. Depending on
your choices of output options above, the views will include trace
files or only contig sequences. However, the calculation of the
contig is carried out the same way, no matter how the contig is
displayed.
See View
and edit contigs on how to use the
resulting contigs.
![]() )|
Assemble Sequences (
)|
Assemble Sequences (![]() )
)
![]() ) tool under De Novo Sequencing (
) tool under De Novo Sequencing (![]() ) in the Toolbox instead.
) in the Toolbox instead.
