Workflows - an overview
CLC Cancer Research Workbench offers a number of analysis workflows, also referred to here as the pre-installed ready-to-use workflows, which include all the necessary steps for a particular analysis, from the initial quality checking and trimming of the reads to the final reporting of the results, for example, the disease causing mutations detected in an analysis. The workflows are easy to use and just require the sequence data as input. You may need to provide additional information relevant to your data and analysis to run a given workflow, for example adapter trim lists for trimming sequences, or, when performing "Targeted Amplicon Sequencing", a description of the sequenced regions.
Irrespective of the type of sequencing data you wish to analyze, there are only few steps necessary before the identified variants are available for your inspection. A schematic representation of the flow that an analysis could take is shown in figure 2.6.
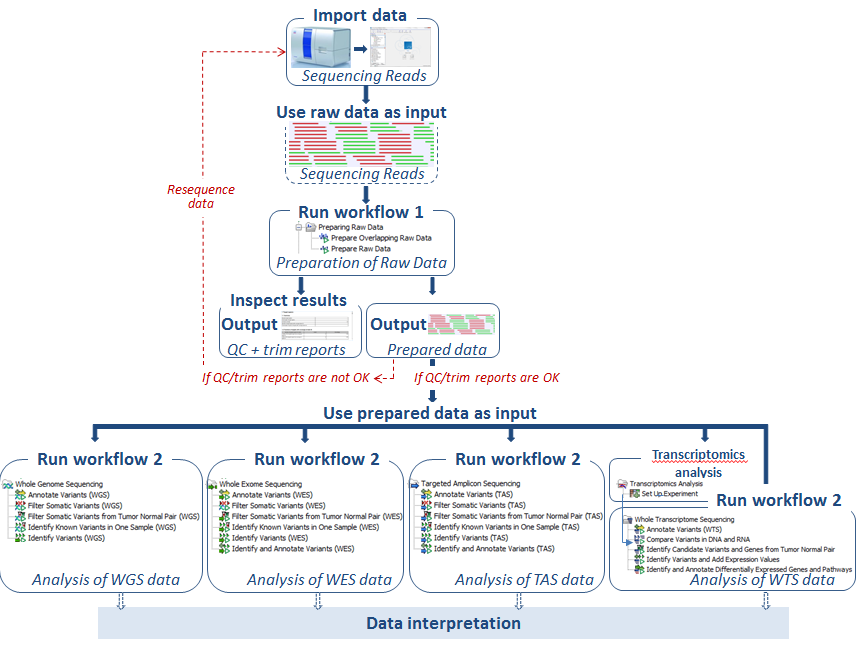
Figure 2.6: A basic example of the flow of steps for a sequencing data analysis. The data is first imported into the Workbench. Then it should be prepared for analysis. Here, a ready-to-use workflow labeled workflow 1 is used for this. It runs quality control and trimming steps. After inspection of the quality and trimming reports, the trimmed data are used as input for another ready-to-use workflow, called workflow 2 in this figure. This is where the data analysis is carried out. Here, workflow choices associated with variant detection are shown. Additional analyses can be performed downsteam of this if desired. Downstream analysis could involve using another ready-to-use workflow or could involve running individual tools from the Tools section of the Toolbox.
The ready-to-use workflows to run, and how many of them to run depend on the type of data you have and the analysis you wish to perform. For example, overlapping paired data involves other considerations than single or non-overlapping paired data. Different workflows will be relevant if your aim is to detect variants or annotate variants with information from other databases. Typically you will need to run two or three workflows to complete a full analysis that includes preparation of the raw data.
The ready-to-use workflows can be divided into four categories:
- Preparing Raw Data The overall purpose of this step is to perform quality control (QC) of the reads, trim the reads whenever relevant, and when working with reads containing overlapping pairs, merge the reads at this step. At this step you must choose the appropriate workflow based on the read types you are working with.
The available "Preparing Raw Data" ready-to-use workflows are:
- Prepare Overlapping Raw Data: Performs quality control and trimming of the sequencing reads and merges overlapping read pairs. This workflow generates five different outputs:
- QC graphic report
- QC supplementary report
- Trimming report (the trimmed sequences will be used directly and automatically as input for the merging of paired reads step).
- Merged reads output
- Not merged reads output
- Prepare Raw Data: Performs quality control and trimming of the sequencing reads. This workflow generates five different outputs:
- QC graphic report
- QC supplementary report
- Trimming report
- Trimmed sequences output
- Trimmed sequences (broken pairs) output
- Prepare Overlapping Raw Data: Performs quality control and trimming of the sequencing reads and merges overlapping read pairs. This workflow generates five different outputs:
- Data analysis This includes the identification and calling of variants. The "Identify Variants" workflow performs read mapping and variant calling. The workflow also includes a quality control of the read mapping and removal of false positives. Optionally you can choose to extend your analysis with an "interpretation" step.
The available tool for data analysis is:
- Identify Variants
- Interpretation At this step you can annotate, filter and compare the variants, that were identified in the data analysis step.
The available tools for data interpretation are:
- Annotate Variants
- Filter Somatic Variants
- Filter Somatic Variants from a Tumor Normal Pair
- Data analysis and interpretation This type of workflow combines both data analysis and the interpretation and includes variant calling, annotation, filtering and comparison of variants.
The available tools for data analysis and interpretation are:
- Identify and Annotate Variants
- Identify Known Variants in One Sample
You can find a detailed description of what the individual workflows can be used for in Analysis of sequencing data.
Figure 2.7 shows all the ready-to-use workflows, available for each application. Irrespective of the application type, the first step involves preparation of the raw data. The ready-to-use workflow to choose to launch the data preparation depends on the type of data being analyzed. For example, the "Prepare Overlapping Raw Data" workflow is designed to handle reads with overlapping pairs, whereas the "Prepare Raw Data" workflow is for read sets without overlapping pairs. The initial data preparation step involves quality control and trimming of the reads.
Figure 2.7: The available pre-installed ready-to-use workflows for the individual application types.
