How to run the Align Contigs tool
The best way to perform the contig alignment depends on the problem to be solved. One way to start is to align all contigs from a de novo assembly to a known or related reference. How to perform a de novo assembly is explained in the CLC Genomics Workbench manual, which can be accessed at:
http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=_CLC_de_novo_assembly_algorithm.html.
It is possible to align contig sequences to multiple references and contigs both with and without reads mapped to them. If a read mapping is used as input for the Align Contigs tool, the consensus sequence will be used for the alignment. However using the consensus of a read mapping can be slow in some cases so if no manual editing of the input read mapping has been performed, consider mapping the reads using "Map Reads to Contigs". This chapter will be focusing on how to perform a contig alignment when a reference sequence is available.
To run the Align Contigs tool:
Toolbox | Genome Finishing Module (![]() ) |
Align Contigs tool (
) |
Align Contigs tool (![]() )
)
This opens the dialog shown in figure 2.1.
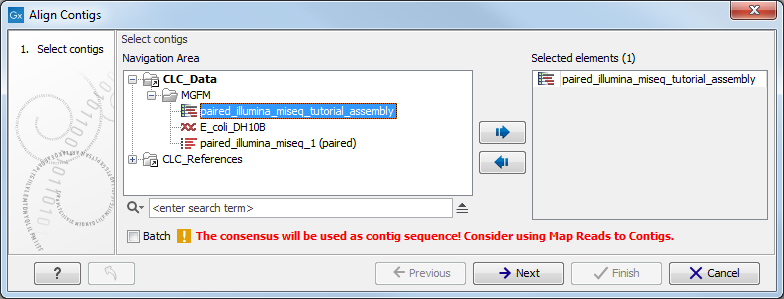
Figure 2.1: Select one or more contigs to analyze.
Select the relevant file containing the contigs and click Next. This leads to the Select contig mapping parameters step shown in figure 2.2.
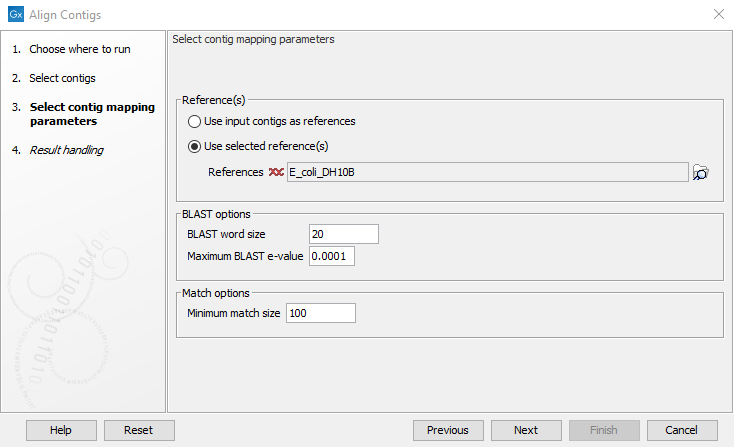
Figure 2.2: Select the contig mapping parameters.
The parameters to be specified in this step are:
- Reference(s)
- Use input contigs as reference. If no reference sequence is available, the contigs can be aligned using themselves as a reference.
- Use selected reference(s). When a reference sequence is available, the contigs can be aligned to the reference. Reference sequence(s) can be selected by clicking on the folder (
 ).
).
- Blast options
- BLAST word size. Specifies the minimum number of nucleotides that must be fully preserved before BLAST finds a match. Using a small value increases the sensitivity but will also report more random matches and slow down the BLAST search on large data sets.
- Maximum BLAST e-value. The BLAST e-value describes the number of hits that are expected by chance. Hence, this option specifies the maximum e-value of matches from BLAST to be included in the alignment.
- Match options
- Minimum match size. Specifies the minimum match size allowed in the alignment.
After the Result handling step, click Finish.
Note! When contigs are used as reference(s) the most interesting matches are often small overlaps between contig ends. To avoid that such small overlaps are filtered out due to a high e-value, contig ends are aligned in a separate step. The alignment of contigs ends considers matches of length ![]() 8bp and matches that are close to contig ends are considered to be more significant compared to matches far from the ends.
8bp and matches that are close to contig ends are considered to be more significant compared to matches far from the ends.
